Inflammation of the rectum (proctitis)
What is proctitis?
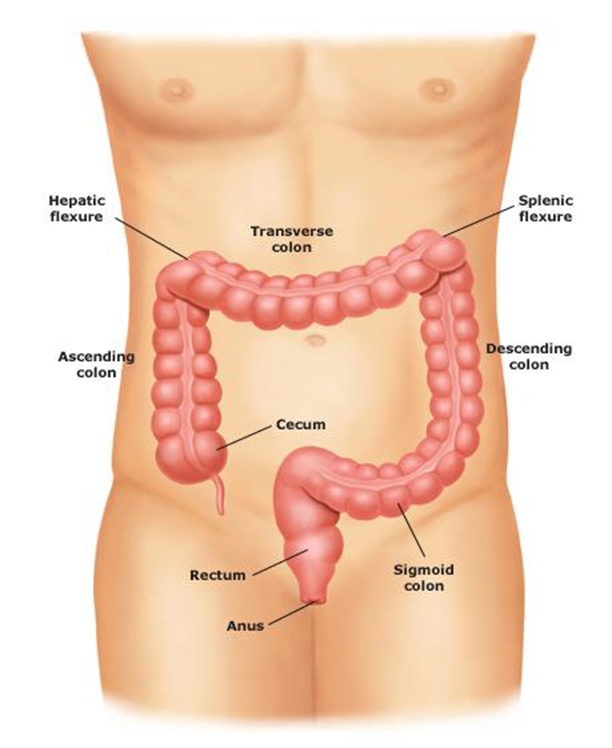
Inflammation of the rectum is called proctitis and is caused by an inflammatory reaction in the rectal mucosa. The lower 15 cm of the bowel is the rectum. If the inflammatory reaction extends higher up it is called colitis.
The symptoms can vary, but often consists of:
- Bleeding and possibly mucus discharge
- Pain during bowel movements
- Tenderness in the rectum
- Feeling of incomplete evacuation of the rectum
- Spasms and cramps during defecation
What causes proctitis?
There are many causes of proctitis:
- Ordinary/common intestinal infections
- Adverse reaction to antibiotics
- Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs - both bacteria and viruses)
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
- Radiation
Common intestinal infections can cause proctitis. The intestinal immune system which is the strongest in the body is activated by foreign bacteria and viruses. The immune system sometimes "overreach" and become too powerful thus damaging the mucosa. The symptoms are usually bleeding and mucus discharge associated with bowel movements.
IBD: see Inflamatory bowel disease
Adverse reaction to antibiotics: most antibiotics kill a vast amount of bacteria, including the "friendly" bacteria, we need in the bowel. In rare cases, disease-causing bacteria survive in large numbers and cause a strong inflammatory response in the bowel/rectum.
STDs: eg. chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, HPV infection, syphilis and HIV. Proctitis from STDs gives tenderness, pain, itching, bloody or pus-like discharge from the rectum and possibly diarrhea.
Virus: Most often caused by the herpes virus, which results in pain, tenderness and discharge. There may be small painful blisters or sores around the anus. In contrast to other cases of proctitis, there may be difficulty in urination, impotence and pain in the buttocks and thighs. Another viral infection is human papilloma virus (HPV), which causes genital warts, which in turn can cause itching, pain, bleeding and discharge.
Proctitis caused by radiation: especially following radiotherapy for prostate cancer in men and cancer of the uterus and cervix in women. The rectum is located close to these organs and is often affected by irradiation. Radiation proctitis causes diarrhea, bleeding and spasms in the rectum/pelvis combined urinary and defecation urge. Symptoms can occur during radiation therapy or immediately after. Radiation proctitis may last from weeks to months, and can also become a chronic condition.
When should I seek medical attention?
If you have pain, bleeding, itching, discharge or changes in stool habits, you should seek medical attention.
How is proctitis diagnosed?
It is mandatory to perform an endoscopy of the rectum and lower part of the colon (a sigmoidoscopy) together with tissue sampling. The tissue samples are sent to a hospital laboratory, and the pathology report is usually available within 10 days. Possibly also blood samples and stool samples must be analyzed. Your doctor will inform you. You can read more about endoscopy on www.raskov.org
How is proctitis treated?
The treatment depends of course on the cause. Since the most common cause of proctitis is infection, antibiotics are usually given in tablet form, together with suppositories. If a STD is suspected, it is important that you undergo tests for clamydia and gonorrhea. If a STD is the case, your partner/partners will have to be treated as well, otherwise the infection will inevitably reoccur.
Genital warts must be removed under local anesthesia and sent for pathological examination.
In case of IBD you must have a prolonged medical treatment. Monitoring and treatment should be followed by a medical gastroenterologist specialist, often in the hospitals outpatient clinic. In these cases the treatment consists of medications that suppress the immune system such as aspirin-like drugs or corticosteroids/steroids.
Surgical treatment of proctitis:
In rare cases, and if the condition is due to an IBD, surgical treatment may be considered. The decision is made by highly specialized doctors in the hospital.
Prevention of Proctitis:
Only the STDs can be effectively prevented by safe sex practices such as condom use. It is only necessary if you engage in high risk sexual behavior such as.:
- Multiple sex partners
- Partner with known STD
- Partners who are i.v. drug addict
- Bisexual or gay partners
- Sex with unknown partner