FODMAP diet

Abdominal pain, flatulence, bloating, constipation/diarrhea, rumbling and belching are often present in gastrointestinal disorders and are difficult to manage and control. These symptoms may be present without disease and are thus called called irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). IBS is a condition rather than a disease. Also read irritable bowel syndrome and intestinal gas & bloating.
If you have been diagnosed with IBS (which requires the exclusion of other intestinal diseases) and experience the problems mentioned above, you should consider a diet with low levels of poorly digestible sugars so-called fermentable oligo-, di-and monosaccharides and polyols (FODMAPs) as FODMAPs ferment in the colon and produce a lot of gases, rumbling and abdominal pain.
To assess your tolerance/intolerance of these naturally occurring, and otherwise completely harmless substances, foods with high levels of FODMAPs are partly or completely removed from your diet for 6-8 weeks and then gradually reintroduced. If you are very thin or underweight, you should only go ahead with the acceptance of your doctor or dietitian, as you may experience weight loss. After 6 weeks, reintroduce 1 food item every 4th day. If symptoms reoccur stop reintroducing new foods for 2 weeks. The goal is to identify the foods that cause problems, and find the limit at which you can eat FODMAPs without problems.
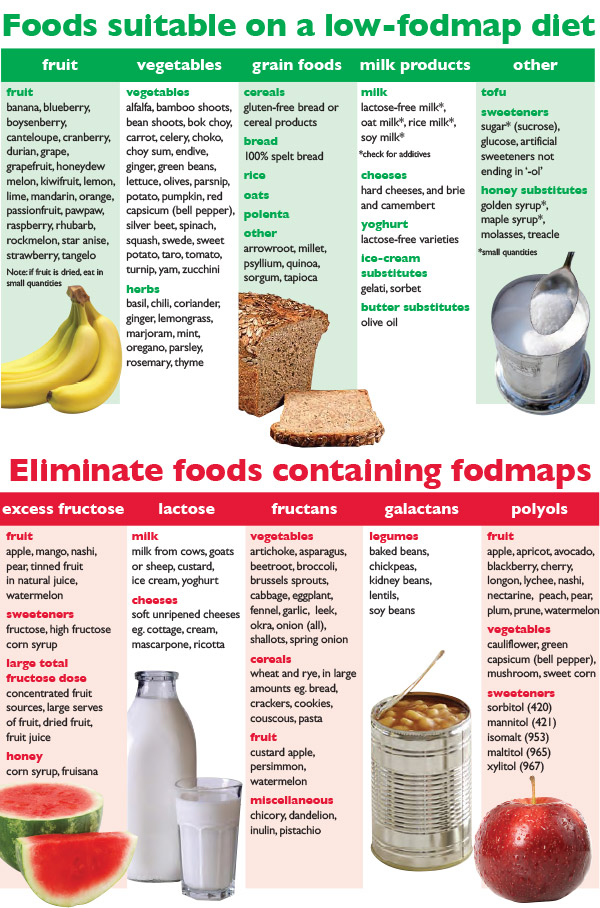
The FODMAPs diet limits the intake of the following sugars (carbohydrates):
- Lactose
- Fructose
- Fructane
- Galactane
- Sugar alcohols (polyols)
Lactose: (milk sugar) is a sugar found in cow's, sheep's and goat's milk. The inability to break down and digest lactose is often called milk allergy, but has nothing to do with allergy. The correct name is lactose intolerance, which is caused by a partial or complete deficiency of the enzyme lactase, which breaks down lactose.
Undigested lactose causes bloating, pain, gas and diarrhea that often occur 30 minutes to 2 hours after ingestion of milk and milk products.
Restrict food with a high lactose content, such as milk, yogurt, ice cream, some cheeses and ricotta. See FODMAP table.
Fructose: (fruit sugar) is a sugar found in fruit, honey and syrup. Not all fructose-containing foods need to be restricted on a low FODMAP diet (see below).
Fructose intolerance is similar to lactose intolerance, in that fructose can not be digested completely due to an enzyme deficiency. Unlike lactose the digestion of fructose is facilitated by the presence of another sugar, glucose, which rarely causes stomach problems.
Therefore foods with a distribution of fructose and glucose of 1:1 or less are generally well tolerated, while foods with higher levels of fructose than glucose (> 1:1), such as apples, pears and mango often will cause IBS symptoms. Restrict food with excess free fructose, see FODMAP table.
Fructanes: Mainly found in vegetables and grains such as onions and wheat. Fructanes are sugars consisting of long chains of fructose molecules which are difficult to digest, because the small intestine lacks an enzyme to break down the chains. Therefore fructanes causes bloating, and abdominal pain. Wheat accounts for the majority of human fructane intake. Limit wheat, onions and garlic along with other vegetables with high fructane content. See FODMAP table.
Galactanes: Mainly found in beans, cabbage and lentils. Galactanes are sugars consisting of chains of galactose molecules. Galactans can not be digested in the intestine for the same reason as fructanse - the gut does not have the enzyme which is needed to break down the molecular chains. Therefore, galactans causes gas, bloating and abdominal pain. See FODMAP table.
Polyols: Polyols are also known as sugar alcohols. They occur naturally in some fruits and vegetables as well as artificial sweeteners like sorbitol, xylitol, mannitol and maltitol. Sugar alcohols can cause the same problems as the sugars above. See FODMAP table.
FODMAPs diet is a challenge:
Use the table below to guide you in your dietary choices. Avoid foods with high FODMAPs content for 6-8 weeks. You should experience an improvement within a week on the FODMAPs diet, but stick to the diet for 6-8 weeks before evaluating the final effect.
If you experience a significant improvement at this time, begin to reintroduce foods with FODMAPs again every 4th day – but only one at a time.
If symptoms reoccur you should remove it or reduce the volume and wait for two weeks before introducing new foods. You may also try one of the specified test foods below.
Test food for each category of sugars:
- Lactose: ½ -1 cup milk
- Fructose: ½ mango or 1-2 tsp honey
- Fructans: 2 slices wheat bread, 1 clove of garlic or 1 serving of pasta
- galactans: ½ cup lentils or chickpeas
- sugar alcohols (polyols): Sorbitol, 2-4 dried apricots, Mannitol, ½ cup mushrooms
Take a look at the table at the bottom of this info. Stick to the foods in the green area and avoid foods in the red area for 6-8 weeks. Afterwards you can try and move foods one at a time from the red area to the green area as described above.
Foods high on FODMAPs can aggravate your stomach problems, but do not misinterpret the problems as being allergy or any other pathological reaction in your body. FODMAPs are not dangerous and the symptoms they cause, are called functional symptoms - they are not an expression of a disease.
Examples of FODMAPs in food:
| Type of food: | High FODMAP content | Low FODMAP content |
|---|---|---|
| Milk | cow, sheep, goat, soy
creamy soups made from milk |
almond, coconut milk, hazelnut milk, rice milk
lactose-free cow's milk lactose-free sour milk lactose-free ice cream |
| Yogurt | cow’s milk yogurt (Greek type is lowest in FODMAPs) Soy yogurt |
coconut milk yogurt |
| Cheese | cottage cheese ricotta cheese marscapone cheese | hard cheeses like cheddar and swiss, parmesan and feta. blue cheese, mozarella and lactose-free cottage cheese |
| Other dairy products | whipping cream sour cream |
Butter
cream cheese |
| Fruit | apple, pear, cherry, raspberry, blackberry,watermelon, nectarine, peach, apricot, plum, prune, mango, papaya, orange juice, canned fruit | banana, blueberry, strawberry, cantaloupe, honeydew, grapefruit, lemon, lime, grapes, kiwi, pineapple, rhubarb, avocado Limit fruit consumption to 1 piece per meal. Prefer fresh ripe fruit. Hard, non-ripe fruit contains more fructose |
| Vegetables | artichoke, asparagus, cabbage, onion, shallots, beans, lentils, hummus, onion powder, garlic, cauliflower | tomato, lettuce, spinach, carrots, cucumber, eggplant, potatoes, water chestnuts, celery, squash, fennel |
| Grains | wheat, rye, barley (large amounts) | brown rice, oats, oat bran, quinoa,corn, gluten-free bread, gluten-free pasta |
| Nuts | pistachios | 10-15 pcs. or max. 1-2 tablespoons of almonds, macadamia, pecan or walnuts, pumpkin seeds,sunflower seeds, sesame, peanuts |
| Sweeteners | honey, agave, syrup, sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol, maltitol | sugar, glucose, sucrose, pure maple syrup, aspartame |
| Alcohol | rum | wine, beer, vodka, gin Limit consumption - all alcohol is irritating to the stomach. |
Examples of FODMAP meals:
Morgenmad
- corn flakes or oatmeal with rice or almond milk, banana and 1 tablespoon sliced almonds
- oatmeal with 1 tablespoon of dried fruit and nuts
- quinoa flakes with rice or almond milk, ¾ cup strawberries and 1 tablespoon pecans
Lunch
- Sandwich with slices of turkey, lettuce or spinach leaves, tomato, cheddar cheese and lactose-free vanilla yogurt with ½ cup blueberries and baby carrots
- fried brown rice or rice noodles, chicken, shrimp or beef, peppers and bok choy, no onion, garlic or dressing
- fruit salad with 1 cup kiwi, strawberries and blueberries. Spinach salad with lemon dressing and cherry tomatoes and brown rice cakes with natural almond butter
Snack
- Pretzels or almond flakes and mozzarella cheese
- Hard-boiled eggs and cherry tomatoes
- Pumpkin Seeds
- Brown rice cakes with natural peanut butter
- banana and almonds
- 1 celery with natural almond butter or
- Carrots and red pepper dipped in tahini
Dinner
- Grilled chicken or salmon with baked sweet potatoes with olive oil or butter, sauteed spinach and peppers seasoned with salt, pepper, a handful of pine nuts and olive oil and a kiwi
- Chicken breast with baked potatoes, salad with homemade dressing without garlic or onion
- Sushi